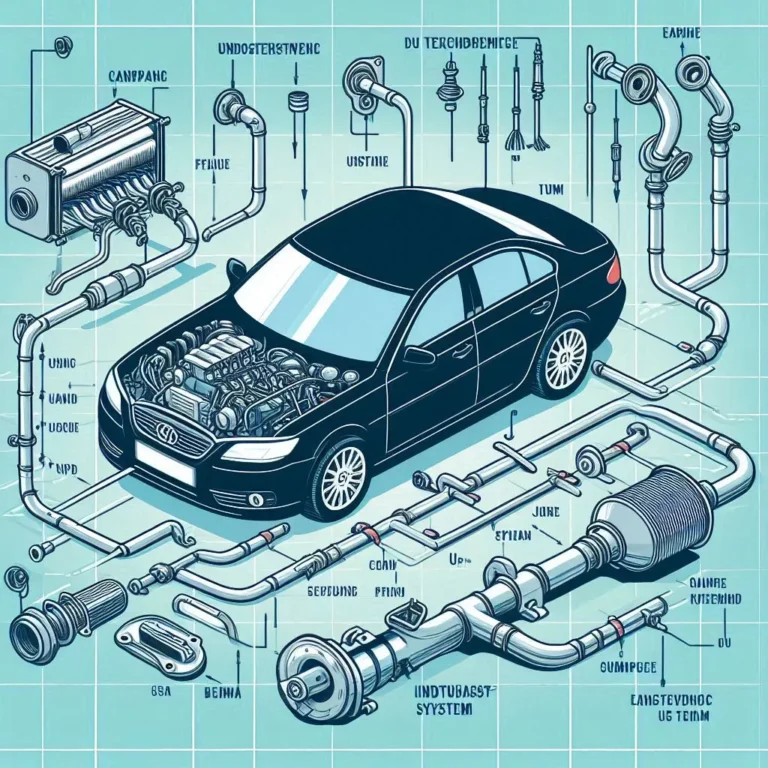
Understanding Your Vehicle: A Complete Car Exhaust Diagram Explained. Every car owner has probably heard the rumble of an exhaust system and felt curious about what’s happening under the hood. Unraveling the mysteries of your vehicle’s exhaust can be surprisingly straightforward once you break it down visually. In this article, we’ll take you on a friendly tour through the “Car Exhaust Diagram,” exploring each component, its role, and how everything works together to keep your ride running smoothly and cleanly.
Car Exhaust Diagram Basics
A Car Exhaust Diagram is essentially a schematic representation of the route exhaust gases take from the engine to the tailpipe. Think of it as a roadmap: it shows you where the gases start, the twists and turns they navigate, and where they finally exit. This visual guide helps drivers, mechanics, and DIY enthusiasts alike understand how different parts connect and why each section matters. In simplest terms, an exhaust diagram highlights the flow of harmful byproducts away from the engine’s combustion chamber, protecting both performance and the environment.
At the heart of the Car Exhaust Diagram is the principle of directing high-temperature gases away from passengers, reducing noise, and converting harmful pollutants into less toxic substances. The path begins at the engine’s exhaust manifold, travels through various pipes and treatment devices, and ends with the familiar tailpipe at the rear of your vehicle.
Car Exhaust Diagram Key Components

Every Car Exhaust Diagram features several essential components. While designs vary by make and model, most systems share the following parts:
- Exhaust Manifold
Attached directly to the engine block, the exhaust manifold collects hot gases from each cylinder and funnels them into a single pipe. Typically made of cast iron or stainless steel, this component must withstand extreme temperatures. (Read More: Car Exhaust Leak Repair: Symptoms and How To Fix It). - Oxygen Sensor(s)
Placed before and sometimes after the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors monitor the level of unburned oxygen in the exhaust. This data helps the engine control unit (ECU) adjust fuel-air mixtures for optimal combustion efficiency and emissions control. - Catalytic Converter
A highlight of any Car Exhaust Diagram, the catalytic converter transforms harmful gases like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances (carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen). Inside, a honeycomb structure coated with precious metals (platinum, palladium, rhodium) facilitates chemical reactions. - Resonator
Some systems include a resonator to fine-tune sound waves before they reach the muffler. Though not present in every model, resonators can help eliminate unwanted frequencies, producing a smoother exhaust note. - Muffler
Often depicted prominently in a Car Exhaust Diagram, the muffler serves to reduce the exhaust noise. Inside, baffles and sound-absorbing materials dissipate sound waves, making your engine’s roar more neighbor-friendly. - Tailpipe
The final segment in any Car Exhaust Diagram, the tailpipe directs the treated gases out of the rear of the vehicle. Often visible beneath the bumper, it can be styled with chrome tips or custom finishes.
Car Exhaust Diagram How It Works
When you press the accelerator, fresh air and fuel mix in the engine’s combustion chamber. After ignition, expanding gases push down the pistons, creating the power that moves your car. These spent gases then enter the exhaust manifold, beginning their three-fold mission:
- Noise Reduction
As gases exit the combustion chamber, they create pressure waves. The muffler and resonator (if equipped) work together to cancel out or absorb these waves, creating a quieter ride. (Read More: Understanding Your Vehicle: A Complete Car Exhaust System Diagram Explained). - Pollution Control
Before meeting the open air, the catalytic converter steps in, breaking down dangerous compounds. This cleaner emission protects both the environment and your compliance with emissions regulations. - Heat Dissipation
Driving exhaust gases away from the engine helps maintain optimal operating temperature and prevents heat damage to nearby engine components.
In a Car Exhaust Diagram, arrows often show gas direction, while labels point out each device’s function. Understanding how these parts interconnect helps diagnose issues quickly and plan maintenance effectively.
Car Exhaust Diagram Common Issues
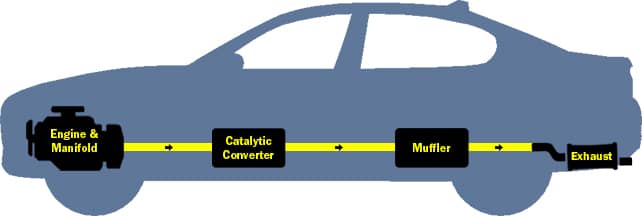
Even the sturdiest exhaust systems can face problems over time. A well-annotated Car Exhaust Diagram can be a mechanic’s best friend when tracking down trouble spots. Here are typical issues to watch for:
- Exhaust Leaks
Cracks in the exhaust manifold gasket or rust holes in pipes can allow gases to escape prematurely. You might notice a ticking sound or a decrease in engine performance. - Clogged Catalytic Converter
Buildup of carbon deposits can restrict gas flow, triggering poor acceleration and increased backpressure. A failing converter often lights up the “Check Engine” warning on your dashboard. (Read More: Electric Vehicles EVs: Shaping the Future of Transportation in 2024). - Faulty Oxygen Sensors
When an oxygen sensor goes bad, the ECU receives inaccurate data, resulting in a rich or lean fuel mixture. You may experience reduced fuel economy and rough idling. - Damaged Muffler
Corrosion or impact damage can create holes in the muffler, leading to louder exhaust noises and potentially allowing water to enter the system. - Loose or Broken Hangers
Rubber hangers and brackets hold the exhaust system in place. If they break, you might hear rattling sounds and observe excessive vibration under the car.
Car Exhaust Diagram Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance can extend the life of your exhaust system and keep things running smoothly. Referencing a Car Exhaust Diagram can guide you through simple checks and DIY inspections:
- Visual Inspection
Look for rust, holes, or cracks along the entire path from manifold to tailpipe. Pay special attention to joints and welds, where corrosion often starts. - Listen for Changes
Unusual sounds—like hissing, rattling, or loud roaring—often signal an exhaust issue. Compare what you hear to the normal engine note you’re used to. - Check for Scents
A strong smell of gasoline or hydrocarbon indicates exhaust gases aren’t being treated properly. It’s best to inspect and replace faulty parts immediately to avoid harmful exposure. - Sensor Diagnostics
Modern vehicles store fault codes whenever sensors detect malfunctions. A basic OBD-II scanner can reveal issues with oxygen sensors or catalytic converters. - Routine Replacement
Many automakers recommend replacing oxygen sensors every 60,000–90,000 miles. Mufflers and resonators might last longer, but check them during routine oil changes.
Car Exhaust Diagram Upgrades and Modifications
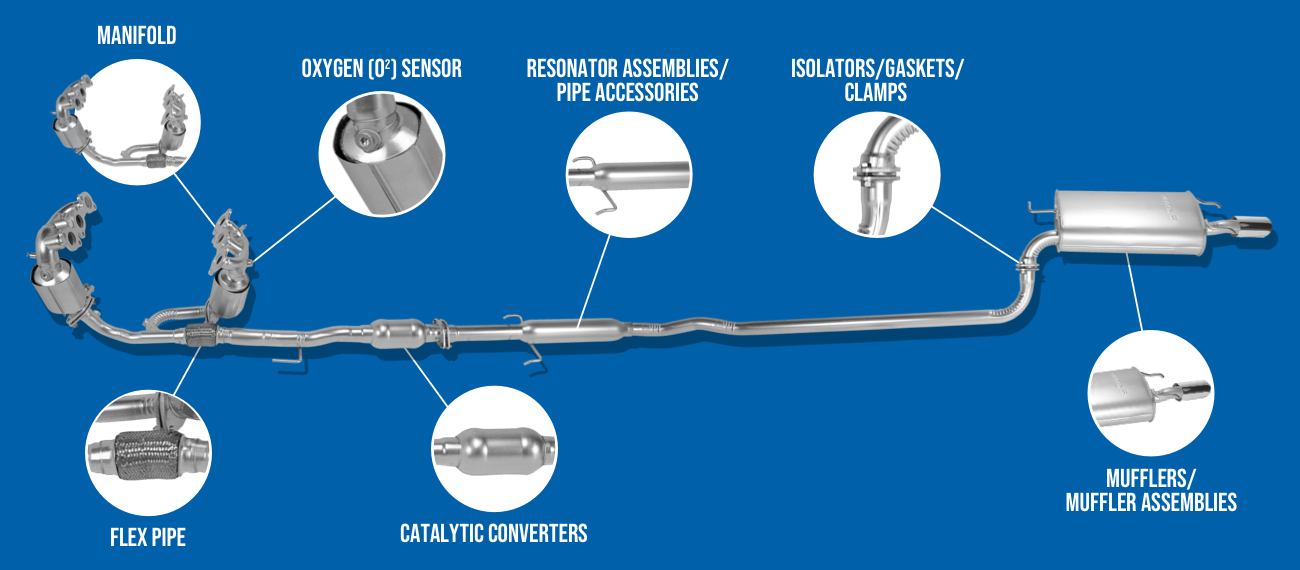
For enthusiasts looking to boost performance or enhance sound, a Car Exhaust Diagram serves as a blueprint for alterations. Here are popular upgrades:
- High-Flow Catalytic Converters
Designed with larger cores, these converters reduce backpressure while still meeting emissions standards. - Aftermarket Exhaust Tips
Swap out stock tips for polished stainless steel or carbon fiber options to give your car a personalized look. - Performance Mufflers
Brands like Borla or Flowmaster offer designs that deliver deeper exhaust notes and marginal power gains through improved gas flow. (Read More: Car Exhaust System Diagram: How It Impacts Performance and Emissions). - Cat-Back Systems
Replacing everything from the converter back, cat-back systems can lighten weight, reduce backpressure, and create a more aggressive sound. - Custom Headers
Upgrading to performance headers can optimize gas flow from the engine, enhancing horsepower and torque. Headers are a prominent feature in any modified Car Exhaust Diagram.
With a solid grasp of your vehicle’s Car Exhaust Diagram, you’re now equipped to talk shop with mechanics, plan maintenance, or embark on performance upgrades with confidence. Whether you’re fixing a leak or seeking a thunderous growl from your tailpipe, this visual roadmap is your best friend under the chassis.